Sperm - structure, production, anomalies
Contents:
Spermatozoa are the male germ cells required for sexual reproduction. In men, they have a length of about 60 microns and are formed in the process spermatogenesis. It lasts about 16 days, but it takes about 2 months to produce all the mature sperm. If infections occur during the first cycle, sperm quality may deteriorate.
Watch the video: "Looks and sex"
1. Sperm - structure
Fully mature spermatozoa are composed of head and neck and their length is about 60 µm. The sperm head is oval in shape. Length about 4-5 microns, width 3-4 microns. Inside, it contains a cell nucleus containing DNA and an acrosome. The acrosome contains proteolytic enzymes responsible for penetration through the transparent membrane of female germ cells. Vitek is an element responsible for the movement of spermatozoa. This element consists of a neck and an insert. The neck is the initial part of the twine and connects the sperm head to the rest of the twine. The insert, on the other hand, is another more subtle element of the sperm structure.
2. Sperm - production
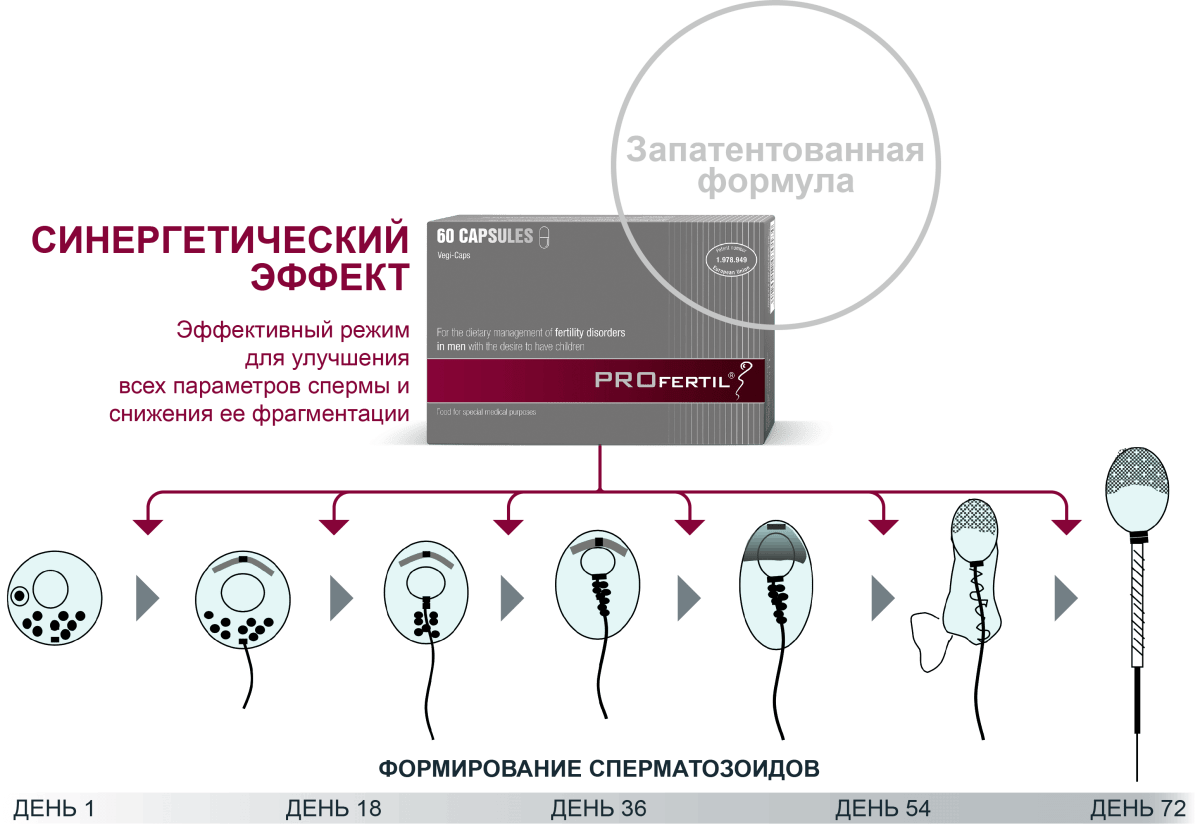
The production of spermatozoa in men is called the process spermatogenesis. During adolescence in boys, cells are formed in the seminal tubes from stem cells after mitosis, which are called spermatogonia. The follicle-stimulating hormone then causes division by mitosis. At this stage, there are spermatocytes order XNUMX. Subsequently, first-order spermatocytes undergo the process of meiosis in which they are formed spermatocytes order XNUMX.
These cells go through the process of meiosis again and form spermatozoa. Then they turn into spermatozoa with a haploid number of chromosomes. During the whole process, the amount of cytoplasm and the number of cell organelles decreases. The nucleus of the cell takes the form of a head, and part of the Golgi apparatus transforms into an acrosome containing the enzymes necessary for penetration into the egg.
The entire process of spermatogenesis is under the hormonal control of testosterone, and the full cycle of human spermatogenesis takes about 72-74 days.
3. Sperm - anomalies
Spermatozoa are the cells necessary for the fertilization process. However, there are various abnormalities that can affect these cells, leading to unsuccessful attempts to conceive. Among these violations, one can single out those that are associated with an abnormal structure, quantity, volume of sperm produced or mobility. As for the structure of spermatozoa, defects can affect all elements of their structure and are called teratozoospermia. Given the number of sperm in the ejaculate, the following may be observed: azoospermia (absence of spermatozoa in the ejaculate), oligospermia (too low sperm count in the ejaculate) and cryptozoospermia (when only single spermatozoa are visible in the ejaculate). Semen volume disorders are divided into: aspermia (when less than 0,5 ml of sperm is released in one ejaculation), hypospermia (if the amount is less than 2 ml), hyperspermia (when the amount of sperm is more than 6 ml). Asthenozoospermia is a term used to describe abnormal sperm motility, while according to current regulations, more than 32% of sperm should show forward movement.
See also: Is humanity waiting for death? Sperm is dying out
Enjoy medical services without queues. Make an appointment with a specialist with an e-prescription and e-certificate or an examination at abcHealth Find a doctor.
Leave a Reply